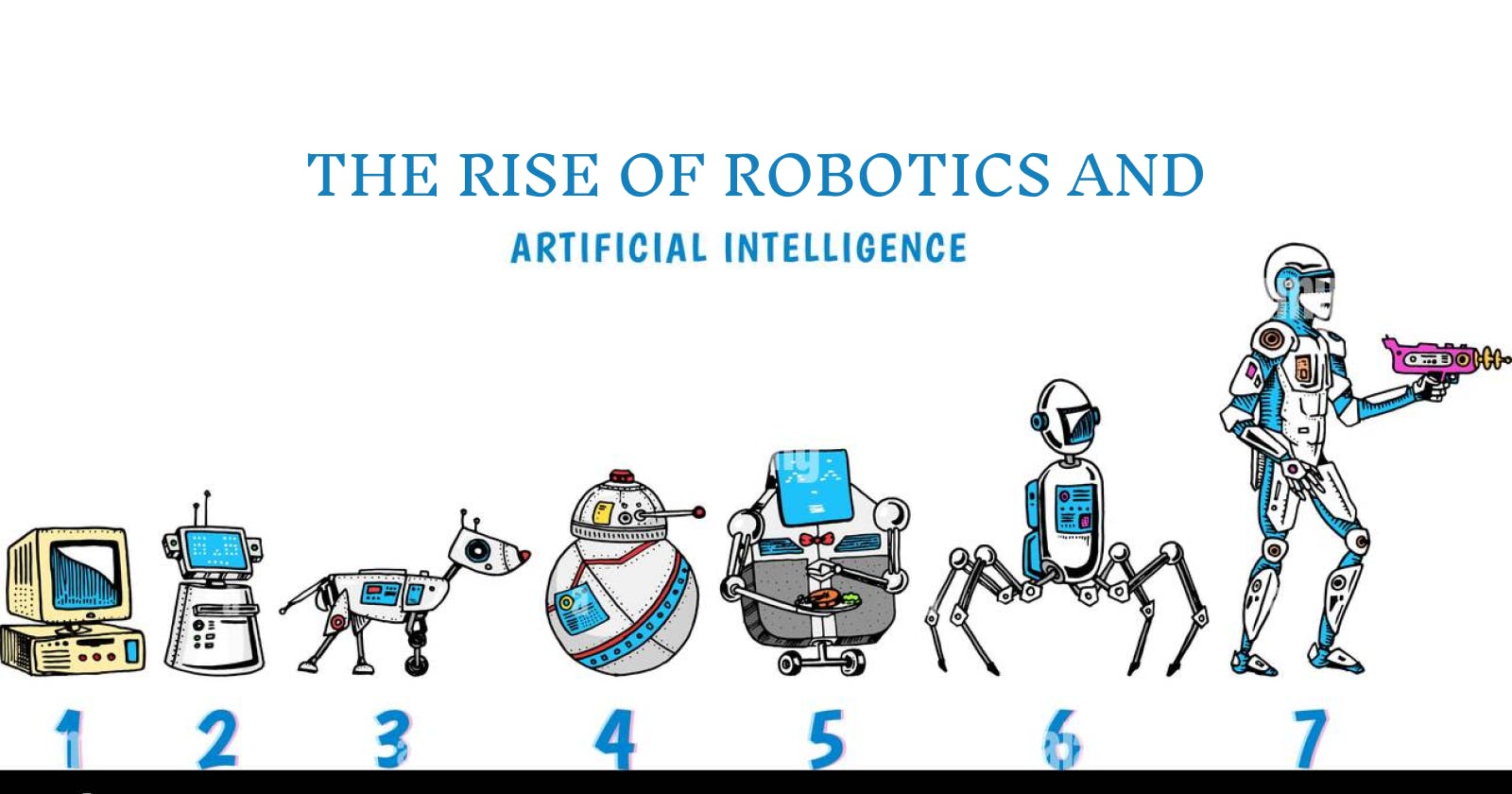
Content
What is Robotics?
What is Artificial Intelligence?
The Beginning - Robotic era
Evolving - Artificial Intelligence
Future
What is Robotics?
Robotics is the branch of technology that deals with the application of robots. Robots are basically machines that are capable of carrying out tasks automatically or semi-automatically, and they are often used in manufacturing and other industries to perform tasks that are often difficult, dangerous or repetitive for human beings. In general, the goal of robotics is to create machines that can assist human activities in various ways.
What is Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial Intelligence refers to the simulation of human intelligence that is programmed to think and act as a human. These machines are designed to learn from their experience and perform human-like tasks. AI can be considered a revolutionary discovery/ invention.
- "AI is the new electricity." - Andrew Ng
The Beginning - Robotic era
The term Robot was first used by the Czech writer Karel Capek in 1921. This was the first step in the major revolution. In 1939, humans were successfully able to create their first robot Elektro. Electro, a humanoid robot, debuts at the World's Fair, smoking cigarettes and blowing balloons.
As there was major evolution going on, Isaac Asimov formulates the Three Laws of Robotics in 1941:
A robot may not injure a human being or through inaction allow a human being to be harmed.
A robot must obey orders given by human beings except where the orders would conflict with the First Law.
A robot must protect its own existence as long as such protection conflicts with the First and Second Laws.
In 1948 William Grey Walter creates the first autonomous robot with complex behaviour and in 2 years Alan Turing published a paper about the possibility of machines that think, develops an idea known as Turing's Test. It tests the machine's ability to "think" by answering a series of questions. In essence, the tester must think the machine's answers are coming from a human. This can be considered the beginning of Artificial Intelligence.
Evolving - Artificial Intelligence
In 1954 George Devol invented the first digitally operated and programmable robot. In about 2 years AI research was founded at a conference at Dartmouth. 2 years later Mark l Perception, a computer that learned new skills by trial and error. In 1968, Mobile robot "Shakey" was introduced controlled by a computer of room size. In 1979 Scara, an articulated robot arm was developed for assembly lines.
In 1984 Doug Lenat and his team start Cyc, to codify millions of pieces of knowledge that compose human common sense. And in the same year The RB5X, developed by General Robotics Corp. which includes software enabling it to learn from its environment. The following year another big event occured where Jaron Lanier's VPL Research Inc. sells the first VR glasses and gloves. He coins this phase as Virtual Reality. In 1986, Honda creates the E0, the first of a series of humanoid robots that walk on two feet. In 1988, Researchers launch Jbberwacky, an AI chatbot designed to learn through conversations.
AI is evolving rapidly, and every day you get to hear about various events now there are lots of AI tools available on the internet for art, creative writing, etc. using these tools saves a lot of time.
Future
As the technology continues to improve, AI will be used in a wider range of applications, from healthcare and transportation to finance and education. It is likely that AI will become an integral part of many industries and will be used to automate many tasks that are currently performed by humans.